Health
True health is achieved by balancing the mind, body, and spirit.
Vitamin D, commonly referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," is a vital nutrient essential for numerous bodily functions, especially maintaining strong bones and a healthy immune system. Produced naturally by our bodies when exposed to sunlight, Vitamin D can also be obtained from specific dietary sources and supplements. Its role in overall health has gained significant attention due to its widespread impact on physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
Vitamin D is unique among vitamins because our bodies can synthesize it through skin exposure to sunlight. It is crucial for:
Vitamin D offers numerous health benefits, including:
Adequate Vitamin D levels prevent bone diseases such as osteoporosis and rickets by ensuring optimal calcium absorption. It is particularly crucial for children during growth periods and adults as they age to maintain bone density.
Vitamin D boosts the body's immune response, potentially reducing susceptibility to common colds, flu, and autoimmune diseases. Studies suggest sufficient Vitamin D levels could decrease the risk and severity of respiratory infections.
Emerging research indicates Vitamin D might have a significant impact on mental health. Low Vitamin D levels are linked to increased risks of depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Adequate Vitamin D may support heart health by helping regulate blood pressure and reducing inflammation, lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Research shows potential benefits in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, indicating that sufficient Vitamin D could help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Sun exposure is the most natural source of Vitamin D. Spending about 10-20 minutes daily in direct sunlight with exposed skin (arms, face, or legs) usually provides sufficient amounts.
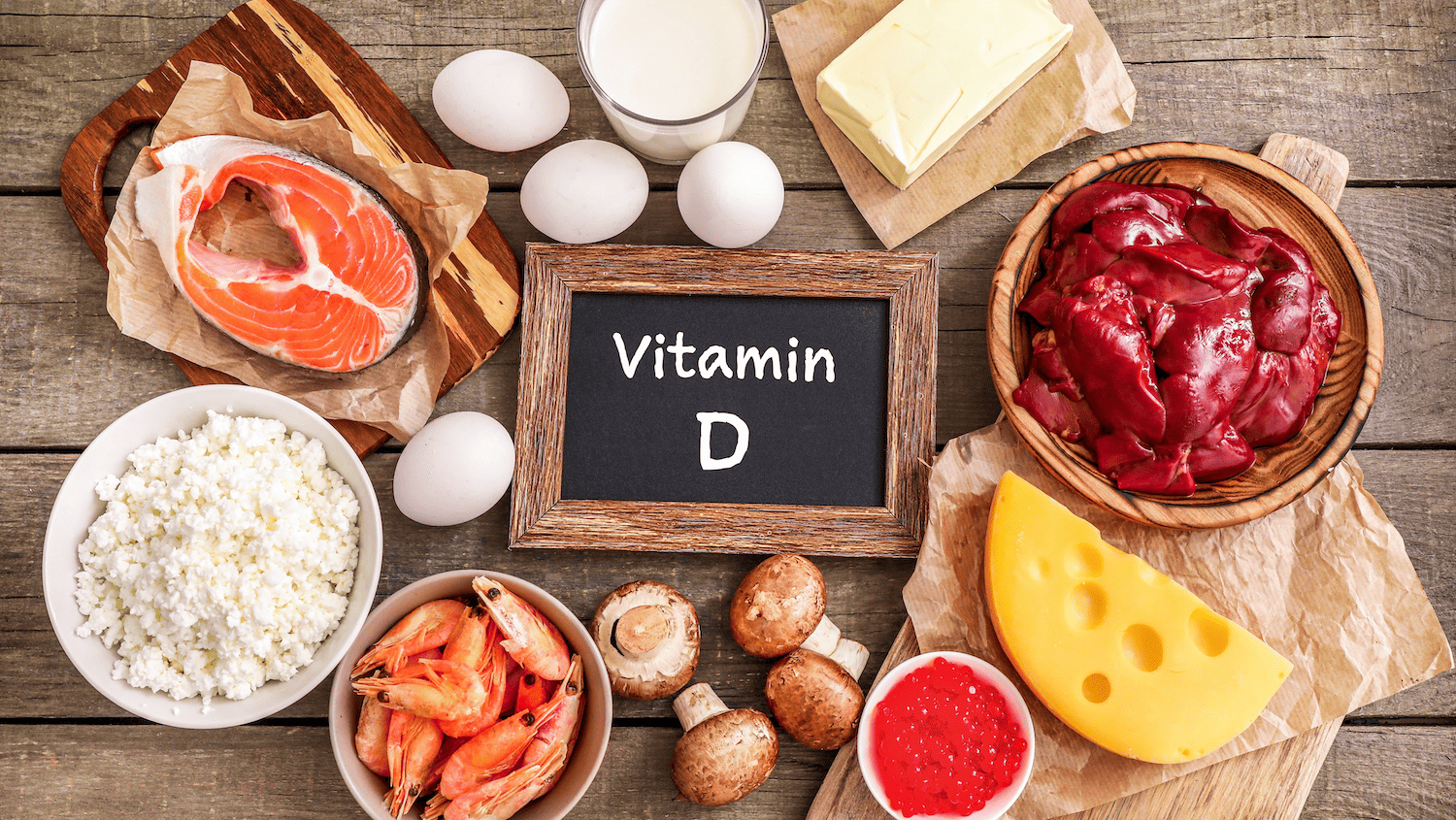
Foods naturally high in Vitamin D include:
Additionally, fortified foods are an important dietary source:
For individuals unable to get enough Vitamin D through sunlight and diet, supplements are widely available and effective. It’s recommended to consult with healthcare providers to determine the appropriate dosage based on individual needs.
Vitamin D deficiency is common, especially among populations with limited sunlight exposure, older adults, individuals with darker skin tones, and those who strictly avoid sunlight. Common signs and symptoms include:
Long-term deficiency can result in serious conditions such as osteoporosis, increased risk of fractures, and even weakened immunity.
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin D varies by age and health status:
Higher doses may be recommended by healthcare providers, particularly for individuals diagnosed with a deficiency or at high risk of deficiency.
While Vitamin D is essential, excessive intake from supplements can lead to toxicity, known as hypervitaminosis D, which may cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, weakness, and serious complications like kidney damage. It's crucial to follow recommended guidelines and medical advice.
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining overall health, from bone strength to immune support. Balancing adequate sunlight exposure, consuming Vitamin D-rich foods, and supplementing, when necessary, can help maintain optimal levels. As always, it's important to consult healthcare professionals to tailor Vitamin D intake to individual health needs and lifestyle factors, ensuring maximum benefit without risk.